- The primary purpose of Lee College is to provide quality instruction for its students. Through a variety of programs and services, Lee College prepares students for success in higher education or employment. Lee College also provides a broad-based program of extension courses, distance education, adult education, continuing education and community service.
School Highlights
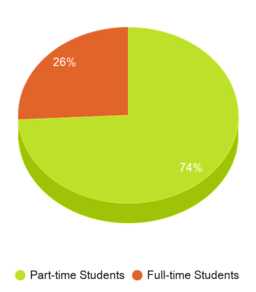
Lee College serves 10,774 students (26% of students are full-time).
The college's student:teacher ratio of 21:1 is lower than the state community college average of 23:1.
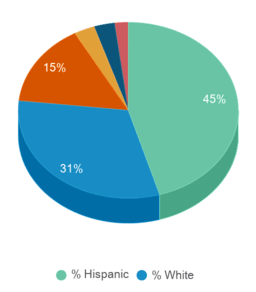
Minority enrollment is 69% of the student body (majority Hispanic), which is less than the state average of 74%.
Quick Stats (2025)
- Enrollment: 10,774 students
- In-state tuition: $2,286
- Out-state tuition: $3,510
- Student:teacher ratio: 21:1
- Minority enrollment: 69%
- Source: Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS)
Top Rankings
Lee College ranks among the top 20% of public schools in Texas for:
Category
Attribute
Affordability
Debt For Students
School Overview
The teacher population of 518 teachers has stayed relatively flat over five years.
Lee College
(TX) Community College Avg.
Carnegie Classification
Associate's Colleges: High Career & Technical-High Traditional
Baccalaureate/Associate's Colleges: Associate's Dominant
Institution Level
At least 2 but less than 4 years
At least 2 but less than 4 years
Institution Control
Public
Private, for profit
Total Faculty
518 staff
262 staff
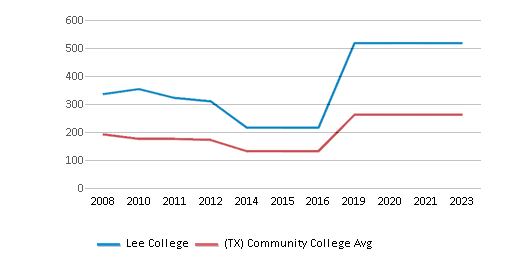
School Calendar
Student Body
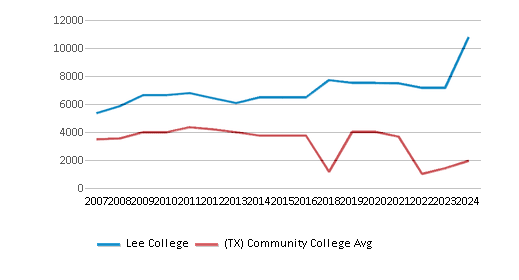
The student population of Lee College has grown by 43% over five years.
The student:teacher ratio of 21:1 has increased from 14:1 over five years.
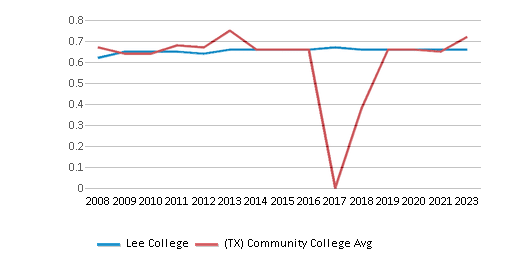
The Lee College diversity score of 0.68 is less than the state average of 0.70. The school's diversity has stayed relatively flat over five years.
Total Enrollment
10,774 students
1,396 students
Student : Teacher Ratio
21:1
23:1
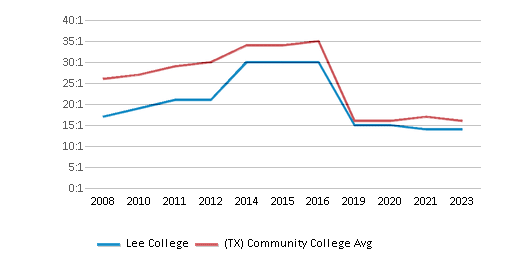
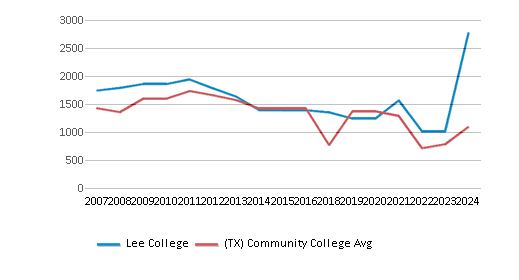
# Full-Time Students
2,779 students
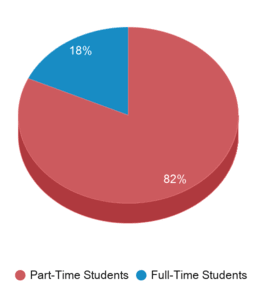
890 students
# Part-Time Students
7,995 students
4,022 students
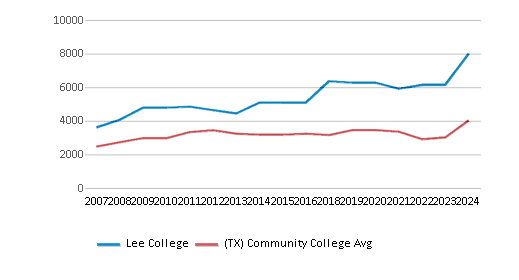
# Enrollment Undergraduate
107 students
403 students
# Full-Time Undergraduate Students
2,779 students
890 students
# Full-Time Graduate Students
n/a
40 students
# Part-Time Undergraduate Students
7,995 students
4,022 students
# Part-Time Graduate Students
n/a
47 students
Total Dormitory Capacity
n/a
252 students
% American Indian/Alaskan
n/a
n/a
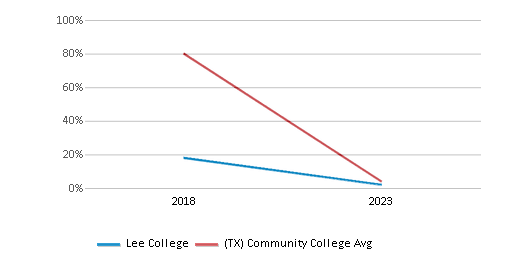
% Asian
2%
6%
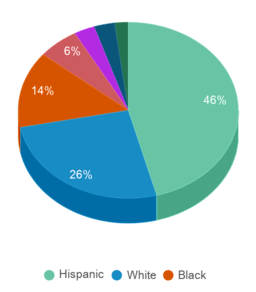
% Hispanic
45%
46%
% Black
15%
14%
% White
31%
26%
% Two or more races
3%
3%
% Non Resident races
n/a
2%
% Unknown races
3%
3%
Diversity Score
0.68
0.70
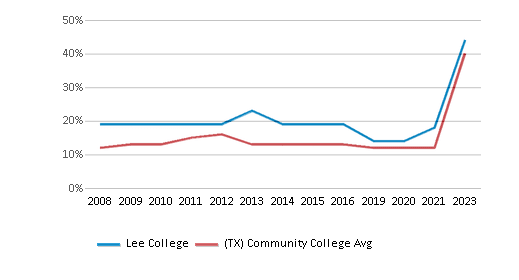
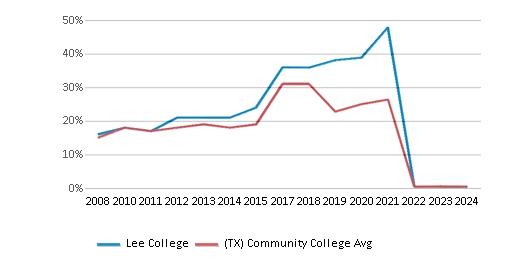
College Completion Rate (Students who graduate in less than 4 years)
0.4029%
0.5469%
College Completion Rate (Students who graduate in 4 years or more than 4 years)
n/a
0.3357%
Average Graduate Earnings (10 Years)
$35,800
$34,600
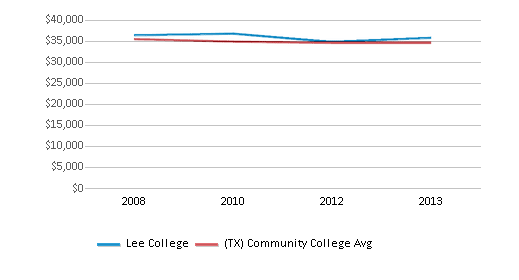
Tuition and Acceptance Rate
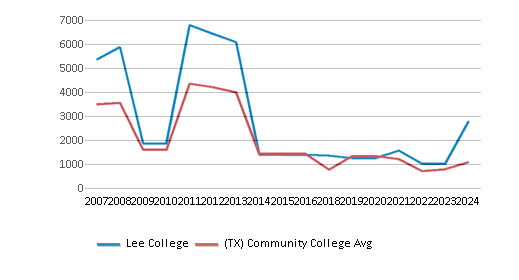
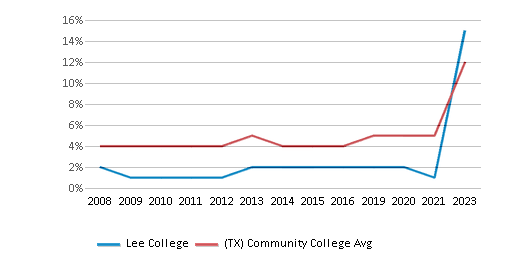
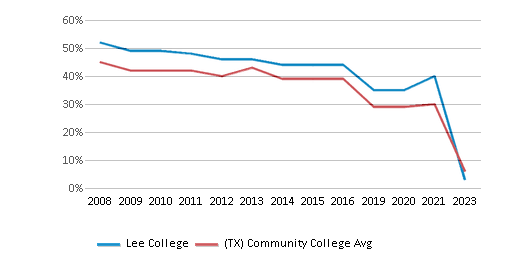
The public in-state tuition of $2,286 is less than the state average of $3,316. The in-state tuition has declined by 39% over four years.
The public out-state tuition of $3,510 is less than the state average of $5,750. The out-state tuition has declined by 18% over four years.
In-State Tuition Fees
$2,286
$3,316
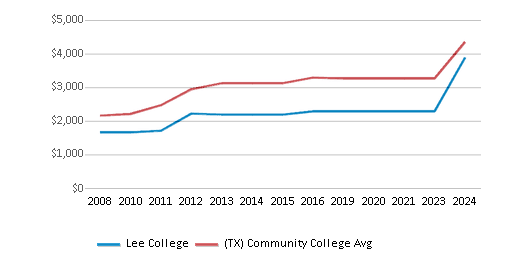
Out-State Tuition Fees
$3,510
$5,750
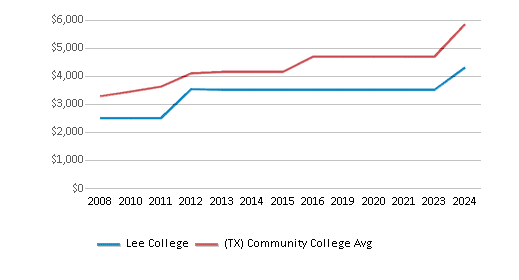
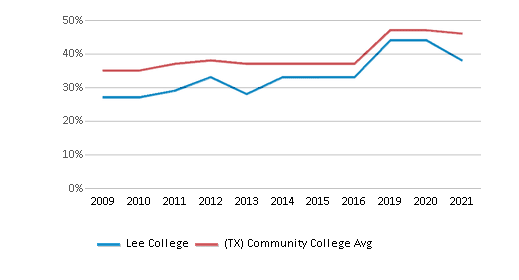
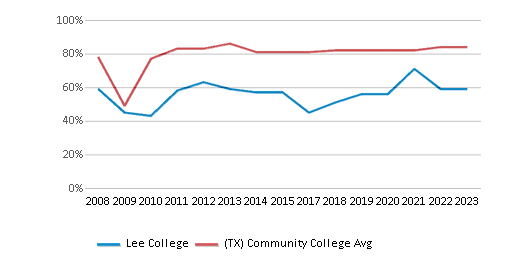
% Students Receiving Some Financial Aid
59%
84%
Median Debt for Graduates
$8,000
$10,765
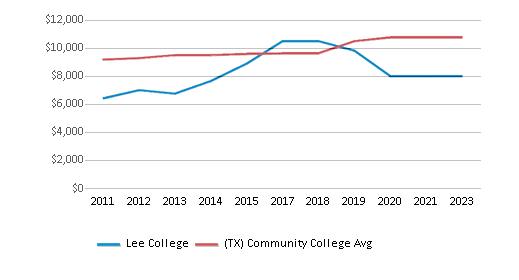
Median Debt for Dropouts
$5,500
$5,500
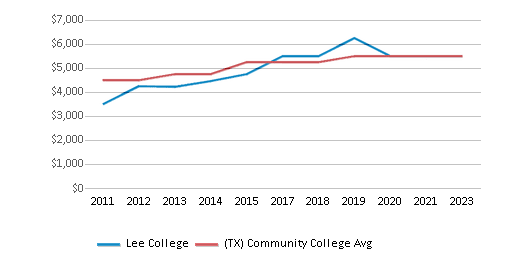
Acceptance Rate
n/a
81%
Source: 2024 (or latest year available) Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS) , School Administrators
School Notes
- Established in 1934 to provide high quality education at a minimal cost, Lee College has continued that tradition for over 60 years. Originally housed on the Robert E. Lee High School campus, Lee College severed its initial integration with the Goose Creek Independent School District under the leadership of the college's first dean, Walter Rundell. In 1948, the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools granted Lee College accreditation and recommended that the college develop its own campus apart from the local high school. A successful bond election in the following year allowed for the construction of Rundell Hall and the campus gymnasium. The college experienced tremendous growth after classes began in the new buildings in 1951. In 2000, another successful bond election led to expansion of the campus by more than 33% with the addition in 2002 of a new Advanced Technology Center, Library, and Tennis Courts. In 2003, the College occupied a new Wellness Center and Sports Complex. Parking was also expanded and beautification efforts including a central courtyard, covered walks, and landscaping were completed. Lee College is accredited by the Commission on Colleges of the Southern Association of Colleges and Schools to award Associate of Arts Degree, Associate of Science Degree and the Associate of Applied Science Degree. Lee College is also accredited by the Texas Higher Education Coordinating Board and the Texas Education Agency.
Frequently Asked Questions
How much does Lee College cost?
Lee College's tuition is approximately $2,286 for In-State students and $3,510 for Out-State students.
What is Lee College's ranking?
Lee College ranks among the top 20% of community college in Texas for: Least expensive tuition and Least debt for graduating students.
Recent Articles

Obtaining Your Bachelor's Degree at a Community College
Explore the evolving landscape of community colleges offering bachelor's degrees, addressing affordability, accessibility, and workforce needs.

A to Z of Community College Certificates and Courses
From business and healthcare to technology and skilled trades, the article showcases the breadth of options available to students seeking to enhance their knowledge, develop new skills, or pursue career advancement.

What is a Community College?
This comprehensive guide explains what a community college is, its history, and its role in higher education. It covers the types of programs offered, differences from four-year colleges, benefits of attending, and important considerations for prospective students, providing valuable insights for those exploring educational options.









